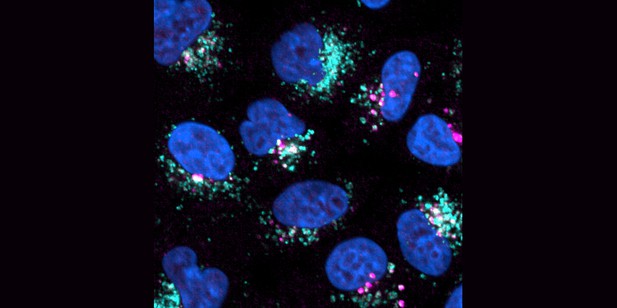
The membrane of damaged lysosomes (cyan) shows an increased phosphorylation of Rab10 (magenta), one of the LRRK2 enzyme’s targets. Image credit: Wang, Bondar et al. (CCBY 4.0).
Lysosomes are cellular compartments tasked with breaking down large molecules such as lipids or proteins. They perform an essential role in helping cells dispose of obsolete or harmful components; in fact, defects in lysosome function are associated with a range of health conditions. For instance, many genes associated with an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease code for proteins required for lysosomes to work properly, such as the kinase LRRK2.
Previous work has shown that this enzyme gets recruited to the surface of damaged lysosomes, where it can modulate the function of another set of molecular actors by modifying them through a chemical process known as phosphorylation. Such activity is increased in harmful versions of LRRK2 linked to Parkinson’s disease. However, the molecular mechanisms which control LRRK2 activity or its recruitment to lysosomes remain unclear.
To examine this question, Wang, Bondar et al. first performed a targeted screen to identify proteins that can regulate LRRK2 activity. This revealed that Rab12, one of molecular actors that LRRK2 phosphorylates, can in turn modulate the activity of the enzyme. Further imaging and biochemical experiments then showed that Rab12 is recruited to damaged lysosomes and that this step was in fact necessary for LRRK2 to also relocate to these compartments. The data suggest that this Rab12-driven recruitment process increases the local concentration of LRRK2 near its Rab targets on the membrane of damaged lysosomes, and therefore leads to enhanced LRRK2 activity. Crucially, Wang, Bondar et al. showed that Rab12 also plays a role in the increased LRRK2 activity observed with two Parkinson’s disease-linked mutations (one in LRRK2 itself and one in another lysosomal regulator, VPS35), suggesting that increased LRRK2 concentration on lysosomes may be a conserved mechanism that leads to increased LRRK2 activity in disease.
Overall, these results highlight a new, Rab12-dependent mechanism that results in enhanced activity at the lysosomal membrane with variants associated with Parkinson’s disease, and for LRRK2 in general when lysosomes are damaged. This knowledge will be helpful to develop therapeutic strategies that target LRRK2, and to better understand how increased LRRK2 activity and lysosomal injury may be linked to Parkinson’s disease.




